Formal and Informal Words (in the English Language)

You don’t talk to your boss the same way you talk to your best friend. Everyone switches between formal and informal language in everyday conversations.
The same is true for writing: some situations call for informal language while others call for more formal vocabulary.
Today, we’re talking about the difference between formal and informal words in English.
How ProWritingAid Can Help with Formal Writing
Using formal English can be difficult because it’s not how we normally speak. It’s easy to miss informal words in your formal writing.
ProWritingAid can point out instances where you’ve used informal words and offer suggestions to replace them with formal words.
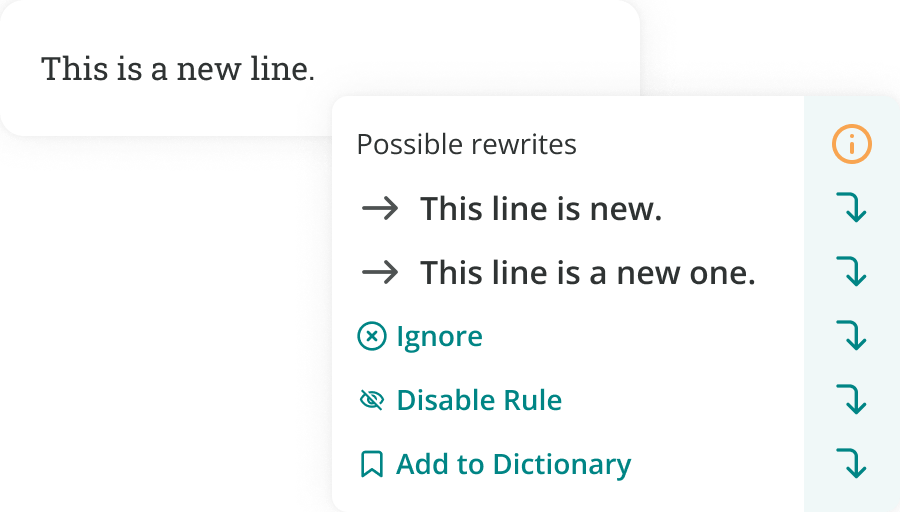
Use the Paraphrase Report to rewrite your work with better wording. When you run this report, you’ll see formal alternatives to your original text.
Formal vs. Informal Language: What’s the Difference?
Words have denotations, or dictionary definitions, and connotations, which are the ideas and feelings a word evokes. Part of a word’s connotation is whether it feels formal or informal.

Most of the time, we speak, think, and write in informal language. But sometimes we need to use formal English, particularly for professional or academic purposes.
There’s a high degree of nuance for determining whether a word is formal.
Some of this knowledge comes from being a native English speaker, which means that learning formal and informal language is tricky for non-native speakers.
But some words are harder to determine even if you’ve grown up speaking English.
While this isn’t an exhaustive list, we’ve done our best to provide plenty of examples of informal and formal language.
Formal Language (with Examples)
Situations where you might use formal language include the workplace and school. Business communication, like emails or memos, require formal language, as does academic writing.

Any writing that is “official,” whether for personal business, government communication, or legal situations, requires formal words and phrases.
For example, if you’re hiring a contractor to remodel your kitchen, think of this as a professional situation. Do you need to send a letter or documents to a lawyer? This is a formal situation.
In addition to word choice, one feature of formal language vs. informal language is the use of contractions. We use considerably fewer contractions in formal writing; we also use standard English grammar structures.
Let’s look at some examples of formal writing.
In a cover letter: I believe I will be an asset to your company. I have attached my resume and references. Thank you for your consideration. I look forward to hearing from you.
To a contractor: I am checking in on the progress with my kitchen remodel. Please provide an updated cost estimate and timeline. Thank you.
Informal Language (with Examples)
We use informal writing all the time in social media posts, text messages, and even blog posts. If you’re emailing or chatting with a friend or family member, you’ll likely use informal expressions and words.

Informal language doesn’t mean slang; slang and colloquial language are a type of informal language.
While you might only use these with the people closest to you, you can use other informal words in many situations, like unofficial conversations with coworkers, emails to customer service, or even networking conversations.
Where formal language sounds stiff, informal language is conversational. Here are a couple of examples of informal writing.
Customer service ticket: I’m really not sure what the issue is. The app keeps glitching, and it’s so frustrating! I added a couple of screenshots. I need this for work, so can you help me ASAP? Thanks!
Professional Social Media Post: So excited about this new joint venture with OtherBusiness! Can’t wait for you to see what we’ve been cooking up!
Even when you use standard English grammar and fewer contractions, knowing which words are formal is difficult. To help, we’ve provided examples of formal and informal words divided by word types.
Verbs: Formal and Informal Words
This list includes common informal verbs or verb phrases, along with their formal counterparts. We’ve put the formal words in parentheses.
- Tell me more (elaborate)
- Be done (finished)
- Show (demonstrate)
- Give (provide)
- Make up (fabricate)
- Find out (discover)
- Leave out (omit)
- Point out (indicate)
- Show up (arrive)
- Deal with (handle)
- Put off (postpone)
- Go against (oppose)
- Clear out (vacate)
- Stand for (represent)
- Get rid of (eliminate)
Adjectives: Formal and Informal Words
There are formal and informal adjectives, too. Here are some common examples.
- Huge (enormous)
- Tiny (diminutive)
- Okay (acceptable)
- Friendly (amiable)
- Rude (disagreeable)
- Messed up (damaged)
- Bad (negative)
- Good (positive)
- Rich (wealthy)
- Sad (despondent)
- Old (dated)
- Easy (simple)
- Fast (timely)
- Happy (pleased)
- Cheap (inexpensive)
Transitions: Informal and Formal Words
Transitions are tricky for formal language because we often use them informally as filler words. Sometimes, the best way to turn transitions into formal words is to eliminate them all together.
Here are some formal substitutions for when you can’t eliminate a transition:
- Anyways (at any rate)
- Plus (moreover)
- So (thus)
- Also (additionally)
- But (however)
- Meanwhile (in the interim)
- In a nutshell (in sum)
- Basically (to summarize)
- And then (furthermore)
Learning the difference between formal and informal words can help you communicate better in professional settings.










