
If you want your writing to be clear and effective, you need to conjugate your verbs correctly.
The verb “to be” is an irregular verb, which means it’s trickier to conjugate into the past tense than many other verbs.
It has two past tense forms that many people mix up, was and were.
So, when should you use was and when should you use were?
In general, we use were for the second person pronoun (you), the first person plural (we), and the third person plural (they).
We use was for the first person singular (I) and the third person singular (he/she/it).
However, there are rare situations in which you will need to use were for singular pronouns too, if you’re using the subjunctive mood.
In this article, we’ll explain the grammar rules behind these two verbs and help you remember when to use was and were in your writing.
How to Use Was vs Were Correctly: Grammar Rules Explained
Whenever you’re using a plural pronoun, such as we or they, you should always use the word were. The same is true for the pronoun you, whether it’s singular or plural.
When you’re writing first and third person using a singular subject, such as I or she, you should use was for the past tense and were for the subjunctive mood.

Let’s take a closer look at when we use was vs were.
They Was or They Were?
Because “they” is a plural pronoun, were is the correct choice for the past tense verb of “to be.”
For example, you would say “They were happy to see me,” not “They was happy to see me.”
We Was or We Were?
“We” is a first person plural pronoun. Were is the correct form to be used with “we,” just like it is with “they.”
You would say “We were eating dinner together,” not “We was eating dinner together.”
You Was or You Were?
You is a pronoun that can be either second person singular or second person plural. In both cases, you should use the form were instead of was.
For example, you would say “Samantha, you were fantastic at the meeting today,” or “Hey folks, you were all brilliant at the conference yesterday.”
I Was or I Were?
When the subject of the sentence is “I,” the past tense of “to be” is was.
For example, you would say “I was at home,” or “I was making dinner.”
The only time you would say “I were” is when you’re using the subjunctive mood. The subjunctive mood is a verb form we use to talk about hypothetical situations.
Look out for words like “if,” “wish,” and “as though” to identify a hypothetical situation in a sentence. These words indicate you might need to use the subjunctive conjugation.

For example, you would use were in the sentence “If I were you, I’d accept his offer,” because you’re discussing a hypothetical situation in which you’ve swapped places with the person you’re talking to.
Similarly, you would use were in the sentence “I wish I were braver,” because you’re talking about a fantasy world in which you’re braver than in the real world.
On the other hand, you would use was in the sentence “I was braver when I was younger,” because you are talking about something that really happened. It’s in the simple past tense, so follows the majority rule.

He Were or He Was?
When the subject of the sentence is he, she, or it, the rules are the same as they are for I. You use he was for sentences in the past tense, and he were for sentences in the subjunctive mood.
For example, you would say “He was in charge of the meeting yesterday” if the person you’re describing really was the leader of the meeting.
On the other hand, you would say “He bossed us around as if he were in charge” if he wasn’t the leader. You are describing an unreal situation and therefore should use the subjunctive mood.
Was vs Were in a Sentence
Here are some examples of were and was in English literature, to help you get a better sense of what they sound like in context. See if you can spot the subjunctive examples.
Examples of Was
“She was as tall as I was. But she wore her height with such grace and poise that it made me feel unworthy to share that trait with her.”—F.C. Yee, The Epic Crush of Genie Lo
“She smiled at me then. It was warm and sweet and shy, like a flower unfurling. It was friendly and honest and slightly embarrassed.”—Patrick Rothfuss, The Name of the Wind
“The boy was her son. His name was Uche; he was almost three years old. He was small for his age, big-eyed and button-nosed, precocious, with a sweet smile.”—N.K. Jemisin, The Fifth Season
Examples of Were
“It wasn’t actually the differences between tribes that caused wars. It was the ways in which all people were alike.”—Elizabeth Bear, Range of Ghosts
“This is like when Gabe and I would play games when we were younger—as soon as I got close to winning, he would change the rules on me.”—Maggie Stiefvater, The Scorpio Races
“I will always wish I were hers, and will always want to be only my own. I haven’t found a way yet to make the two fit.”—Rory Power, Burn Our Bodies Down
“My stomach swooped with vertigo, as though I were still descending and had just missed the stair’s final step.”—Margaret Rogerson, An Enchantment of Ravens
“She has the gift of accepting her life; as he comes to know her, he realizes that she has never wished she were anyone other than herself, raised in any other place, in any other way.”—Jhumpa Lahiri, The Namesake
“He felt as though he were looking at a complicated riddle, of which he had once been told the answer but had forgotten it and was always on the point of remembering.”—Dorothy L. Sayers, Whose Body?
Was vs Were: Final Thoughts
If you want to make sure you’re using the subjunctive mood correctly, ProWritingAid can help!
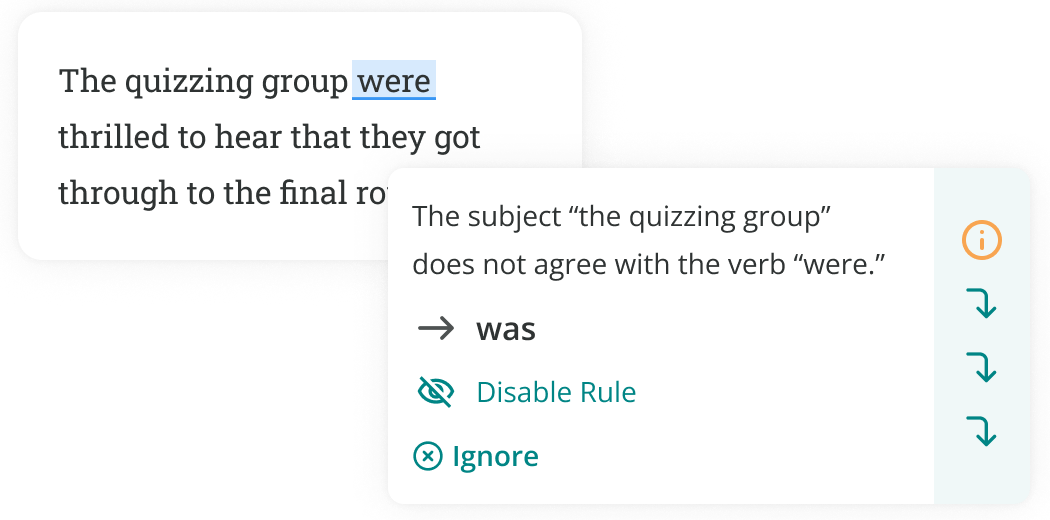
The tool will highlight situations where you need to use were with a singular pronoun like he, she, or I.


