
You may have come across verbs where the past tense isn’t what you’d expect it to be. For example, the past tense of “drive” isn’t “drived,” and the past tense of “beat” isn’t “beated.”
If you’ve seen such a verb that doesn’t fit the typical past-tense pattern, then you’ve encountered something called an irregular verb.
What exactly is an irregular verb?
The short answer is that a verb is irregular if you can’t change it to past tense just by adding “-ed” or “-d” to the end.
In order to use these verbs correctly, you have to memorize their past simple and past participle forms, since they don’t fit into the usual pattern.
This article will explain how irregular verbs work and give you a list of the most common ones in English.
What Is an Irregular Verb?
Let’s start by talking about what a regular verb is. A regular verb is one that forms its past simple or past participle form by adding “-ed” or “-d” to its base form.
For example, “to jump” is a regular verb, because to change it to past tense, you simply add “-ed” to form the word “jumped.”

You would say “I jump over the fence” (present tense), “I jumped over the fence” (past simple), or “I have jumped over the fence” (past participle).
Other examples of regular verbs include:
- to love: “loved” (past simple and past participle)
- to finish: “finished” (past simple and past participle)
- to paint: “painted” (past simple and past participle)
An irregular verb, on the other hand, is any verb that doesn’t follow that rule. Its past simple and/or past participle forms are created in a way that doesn’t involve adding a “-d” or “-ed” at the end.
The verb “to bite” is irregular, because its past tense is “bit,” not “bited.” It breaks the normal rule for how you change a verb to past tense.
You would say “I bite the apple” (present tense), “I bit the apple” (past simple), or “I have bitten the apple” (past participle).

Other examples of irregular verbs include:
- to sleep: “slept” (past simple and past participle)
- to write: “wrote” (past simple) and “written” (past participle)
- to read: “read” (past simple and past participle)
How Many Irregular Verbs Are There in English?
There are over 200 irregular verbs in English. These include some of the most commonly used verbs in the language, such as “to be,” “to have,” and “to say.”
British English actually has more irregular verbs than American English, because some conjugations are spelled differently.
For example, “to spell” is a regular verb in American English, where the past tense is “spelled,” but an irregular verb in British English, where the past tense is “spelt.”
What Are the Most Common Irregular Verbs in English?
Let’s take a look at the most common irregular verbs we use in English.
In the following table, the first column shows you the base form, also known as the infinitive form, of each verb.
The second column shows the past simple tense of the verb. The past simple tense is the conjugation you use to show that an action took place in the past.
The third column shows the past participle of the verb. The past participle is the conjugation you use to show that an action took place prior to some other event, or in a way that has some connection to the present.
| Base Form |
Past Simple |
Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| arise |
arose |
arisen |
| be |
was / were |
been |
| bear |
bore |
borne / born |
| beat |
beat |
beaten |
| become |
became |
become |
| bend |
bent |
bent |
| begin |
began |
begun |
| bend |
bent |
bent |
| bet |
bet |
bet |
| bid |
bid / bade |
bid / bidden |
| bind |
bound |
bound |
| bite |
bit |
bitten |
| bleed |
bled |
bled |
| blow |
blew |
blown |
| break |
broke |
broken |
| breed |
bred |
bred |
| bring |
brought |
brought |
| build |
built |
built |
| burn |
burned |
burnt |
| burst |
burst |
burst |
| buy |
bought |
bought |
| can |
could |
could |
| catch |
caught |
caught |
| choose |
chose |
chosen |
| cling |
clung |
clung |
| come |
came |
come |
| cost |
cost |
cost |
| creep |
crept |
crept |
| cut |
cut |
cut |
| deal |
dealt |
dealt |
| dig |
dug |
dug |
| dive |
dived / dove |
dived / dove |
| do |
did |
done |
| draw |
drew |
drawn |
| dream |
dreamt / dreamed |
dreamt / dreamed |
| drink |
drank |
drunk |
| drive |
drove |
driven |
| dwell |
dwelt / dwelled |
dwelt / dwelled |
| eat |
ate |
eaten |
| fall |
fell |
fallen |
| feed |
fed |
fed |
| feel |
felt |
felt |
| fight |
fought |
fought |
| find |
found |
found |
| flee |
fled |
fled |
| fling |
flung |
flung |
| fly |
flew |
flown |
| forbid |
forbade |
forbidden |
| foresee |
foresaw |
foreseen |
| forget |
forgot |
forgotten |
| forgive |
forgave |
forgiven |
| forsake |
forsook |
forsaken |
| freeze |
froze |
frozen |
| get |
got |
got / gotten |
| give |
gave |
given |
| go |
went |
gone |
| grind |
ground |
ground |
| grow |
grew |
grown |
| hang |
hung |
hung |
| have |
had |
had |
| hear |
heard |
heard |
| hide |
hid |
hidden |
| hit |
hit |
hit |
| hold |
held |
held |
| hurt |
hurt |
hurt |
| keep |
kept |
kept |
| kneel |
knelt / kneeled |
knelt / kneeled |
| know |
knew |
known |
| lay |
laid |
laid |
| lead |
led |
led |
| leave |
left |
left |
| lend |
lent |
lent |
| let |
let |
let |
| lie |
lay |
lain |
| light |
lit |
lit |
| lose |
lost |
lost |
| make |
made |
made |
| mean |
meant |
meant |
| meet |
met |
met |
| overcome |
overcame |
overcome |
| partake |
partook |
partaken |
| pay |
paid |
paid |
| prove |
proved |
proven |
| put |
put |
put |
| quit |
quit |
quit |
| read |
read |
read |
| ride |
rode |
ridden |
| ring |
rang |
rung |
| rise |
rose |
risen |
| run |
ran |
run |
| say |
said |
said |
| see |
saw |
seen |
| seek |
sought |
sought |
| sell |
sold |
sold |
| send |
sent |
sent |
| set |
set |
set |
| shake |
shook |
shaken |
| shine |
shone |
shone |
| shoot |
shot |
shot |
| show |
showed |
shown |
| shut |
shut |
shut |
| sing |
sang |
sung |
| sink |
sank |
sunk |
| sit |
sat |
sat |
| sleep |
slept |
slept |
| slide |
slid |
slid |
| speak |
spoke |
spoken |
| speed |
sped |
sped |
| spend |
spent |
spent |
| spin |
spun |
spun |
| spit |
spat / spit |
spat / spit |
| spread |
spread |
spread |
| spring |
sprang |
sprung |
| stand |
stood |
stood |
| steal |
stole |
stolen |
| stick |
stuck |
stuck |
| sting |
stung |
stung |
| stink |
stank |
stunk |
| strike |
struck |
struck |
| strive |
strove |
striven |
| swear |
swore |
sworn |
| sweep |
swept |
swept |
| swim |
swam |
swum |
| swing |
swung |
swung |
| take |
took |
taken |
| teach |
taught |
taught |
| tear |
tore |
torn |
| tell |
told |
told |
| think |
thought |
thought |
| throw |
threw |
thrown |
| undergo |
underwent |
undergone |
| understand |
understood |
understood |
| wake |
woke |
woken |
| wear |
wore |
worn |
| weep |
wept |
wept |
| win |
won |
won |
| wind |
wound |
wound |
| withdraw |
withdrew |
withdrawn |
| wring |
wrung |
wrung |
| write |
wrote |
written |
How Many Different Types of Irregular Verbs Are There?
You may have noticed that for some of the verbs in the table, all three columns are the same. For others, two of the columns are the same. And for others still, all three of the columns are different.
It can be helpful to think of irregular verbs in different groups depending on how many columns are the same.
You can split irregular verbs into the following four types:
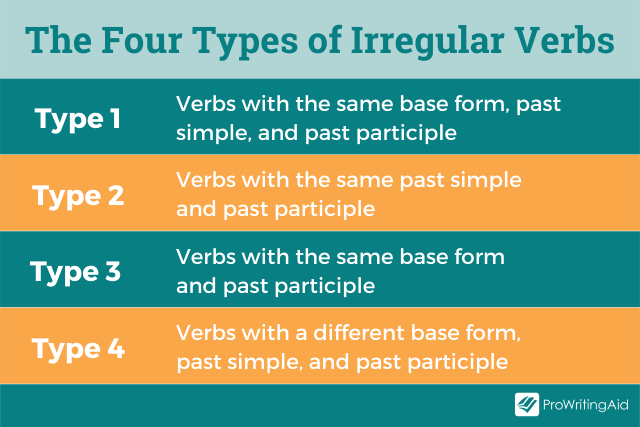
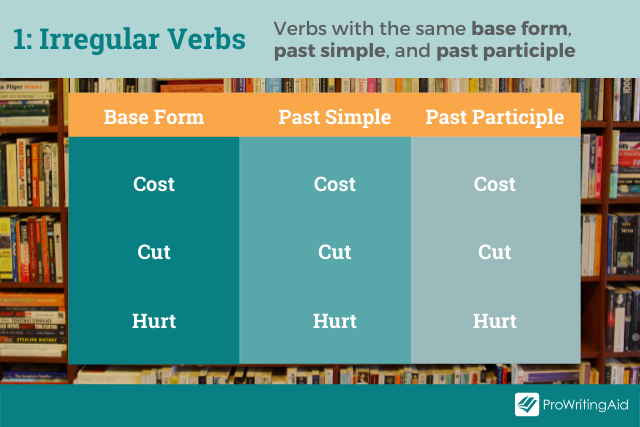
Type 1: Verbs with the Same Base Form, Past Simple, and Past Participle
This type includes irregular verbs for which all three columns are the same.
Examples include “cut / cut / cut,” “hurt / hurt / hurt,” and “put / put / put.”
Type 2: Verbs with the Same Past Simple and Past Participle
This type includes irregular verbs for which the first column is different, but the second and third columns are the same.
Examples include “bring / brought / brought,” “catch / caught / caught,” and “sell / sold / sold.”

Type 3: Verbs with the Same Base Form and Past Participle
This type includes irregular verbs for which the second column is different, but the first and third columns are the same.
Examples include “come / came / come,” “become / become / become,” and “run / ran / run.”

Type 4: Verbs with a Different Base Form, Past Simple, and Past Participle
This type includes irregular verbs for which all three columns are different.
Examples include “begin / began / begun,” “break / broke / broken,” and “write / wrote / written.”
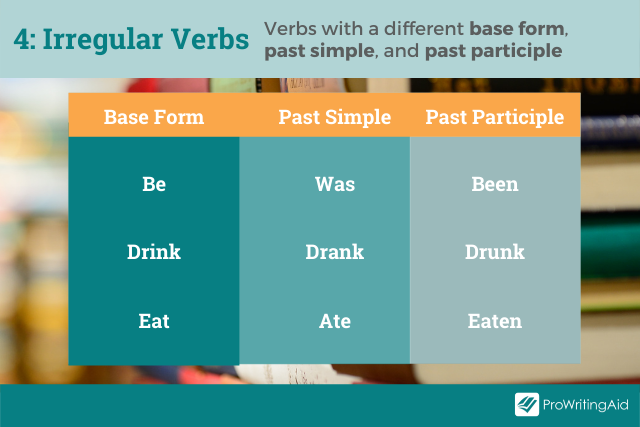
Type 1 is the easiest because you only need to memorize one form that works in all tenses, while Type 4 requires the most memorization.
Using these types, you can easily see how many forms you have to memorize for each verb. It also makes it easier to learn each verb, because you can learn it as part of a pattern.
What’s the Best Way to Learn and Remember Irregular Verbs?
If you’re a native English speaker, you probably have a natural grasp of which verbs are irregular. Most children pick up on these patterns without thinking consciously about them.
If you’re in the process of either teaching or learning English, there’s no easy trick for remembering how to use irregular verbs. Each one is different, and the only way to master them is by memorizing them intentionally.
Extra help is always good. ProWritingAid’s grammar checker will highlight and suggest corrections if you mix up your conjugations.

Sign up for a free ProWritingAid account.
There are various different methods you can use to memorize these words.
One useful method is to use flash cards. If you practice 10 to 15 a day, you can memorize all the irregular verbs in the table within less than a month.
It’s also helpful to pay attention whenever you see a verb that doesn’t have a regular conjugation. Write it down in a notebook and review your notebook words regularly.
Finally, it’s a great idea to practice creating your own example sentences with each new irregular verb you learn. That way, you can start building intuition for how these verbs sound in past tense.

Why Are Some Verbs Irregular While Others Are Not?
Most irregular verbs exist as remnants of older words that have been part of the English language for a long time.
Grammar has changed significantly over the history of the English language, so conjugations worked differently then than they do now. We kept some of those archaic conjugations even after the rules fell out of use.
For example, in Middle English, there used to be a group of verbs for which you created the past tense by shortening the vowel. That’s why the past tense of “keep” is “kept,” the past tense “weep” is “wept,” and the past tense of “leap” is “leapt.”
Final Words
Now you know what irregular verbs are, and you have a table of the most common ones to start memorizing.
Was this article helpful? Let us know in the comments.


