Fare and fair have different meanings, and each of them have several definitions that we'll cover today.
In general, fair can refer to to justice, complexion, or a carnival. It can also be used to describe something that is good.
Fare refers to food, money, or how something is going.
It’s fair to say that some people don’t fare well with the fair amount of differences between "fare" and "fair." That sentence was hard to write. I can’t imagine how it is to read!
This complication exists because fair and fare sound exactly alike, but mean two—well, more than two—different things.
We are going to walk through the various definitions of fair and fare and talk about how to remember which spelling goes with which meaning.
Are "Fair" and "Fare" Homophones?
Before we work on those definitions, though, let’s go through a little refresher for you. Fair and fare are homophones.

Homophones are two or more words that are spelled differently but have the same sound.
Homophones can cause confusion because the only thing that separates them (other than what they mean) is their spelling, which means spelling matters even more than usual. After all, using the wrong spelling can completely change the meaning of the sentence!
Here are some other examples of homophones:
- Too, to, two
- Hear, here
- When, win
- Principal, principle
- Compliment, complement
Now that we are clear on why fair and fare are homophones, let’s start looking at their definitions.
What Does "Fair" Mean?
Not only do you have to keep up with fair versus fare, but you also have to remember the differences between fair versus fair! That’s because, depending on how you use it, fair can be an adjective, adverb, noun, or verb.
Let’s look at each of these in turn.
How Do I Use "Fair" as an Adjective?

An adjective is a word or phrase that is used to describe a noun.
For example, in the phrase “the happy dog,” happy is an adjective that describes the noun (dog).
Fair is an adjective that can mean two things:
1. A just or equitable solution. e.g. We came to a fair resolution. (Where fair is describing the noun resolution.)
2. A light or blonde complexion. e.g. Her hair was long and fair. (Where fair is describing the noun hair.)

How Do I Use "Fair" as an Adverb?
An adverb is like an adjective, but instead of describing a noun, it is used to modify (change) a verb, adjective, or other adverb. The following sentences are examples:
- He speaks quietly. (Quietly is an adverb that describes the verb speaks.)
- Jane is very good. (Very describes the adjective good, which describes the noun Jane.)
- He speaks too quietly, but he is a very good listener. (Too describes quietly and very describes good.)
- Luckily, you were there to catch me when I fell. (Luckily describes the whole sentence.)
You may have been taught that most adverbs end in -ly. Fair is an example of an adverb that doesn’t end in -ly.
When used as an adverb, fair can have another two meanings:
1. Without cheating. e.g. The game was played fair and square. (Fair describes how the game was played.)
2. The extent to check something is happening. e.g. "How is your homework going?" "Fair to middling." (Where fair is describing the homework.)

How Do I Use "Fair" as a Noun?
A noun is a word that names a thing, such as a person, place, or idea. It can be a proper noun, such as Susie or Yellowstone National Park, or it can be more general, such as door, park, girl, etc.
Fair is a noun that refers to the seasonal carnival that might come to your town. e.g. In my hometown, the fair would come every November.
I had a teacher that would combine the definitions of fair to make a witty comment. Whenever anyone complained about the work and said it “wasn’t fair” (as in just), he’d tell us “The fair is in November. Now get back to work!”

However, this actually isn’t the only time fair is used as a noun. Its other noun usage, though, is rarely used. But just in case you enjoy or study medieval literature, in ye olden times, fair could refer to a beautiful maiden. In this sense, it actually acted as a noun:
- He pursueth his fair throughout the land.
These days, the same idea is kind of still around, but fair acts as an adjective. Instead of replacing the word maiden, it describes it.
- He pursued his fair maiden throughout the land.
How Do I Use "Fair" as a Verb?
A verb describes the action of the sentence. Fair as a verb isn’t really used in common speech but it’s still worth defining.
Fair is a verb which means a positive change in the weather, e.g. The rain is starting to fair off a little.
How Do You Use "Fair" in a Sentence?
Here are some examples of fair in a sentence. See if you can figure out if it’s being used as an adjective, adverb, noun, or verb.
- It’s not fair to ask me to do that.
- You have the fairest face in all the land.
- Play fair or don’t play at all.
- Is it fair to say that we’ll see you there?
- Did you see that the fair is back in town?
What Does "Fare" Mean?
Like fair, fare has several different forms, with different meanings. Let’s take a look.
How Do I Use "Fare" as a Noun?
Just like fair, fare can be a noun. However, the good news is that it is much more common this way, so if you are ever in doubt, you may be able to get away with this spelling.
Let’s add in some fare definitions:
1. The cost of transportation. e.g. The bus fare went up last week.
2. The passengers who paid the transportation fee. e.g. The train has a full fare today.
3. A specific kind of food range. e.g. I like Asian fare, but my sister prefers Mexican.

How Do You Use "Fare" as a Verb?
Fare as a verb can be the most confusing because it is so similar to some of the above usages of fair. Below, I have included some tips to tell these apart, but for now, let’s take a look at the definitions:
1. Succeed at or get along with something. e.g. How did you fare on the puzzle?
2. How something went. (The good news is that this one is kind of outdated, so you probably won’t have to ever use it.) e.g. The soldiers fared well in battle.

How Do You Use "Fare" in a Sentence?
Here are examples of fare in a sentence. See if you can tell whether it’s a noun or a verb.
- Do you have enough money for the subway fare?
- Have you eaten at the new restaurant in town? It has really fancy fare.
- How fares your family?
- We fared well in the tournament. We ended up with second place.
- The plane had a small fare. Most seats were still empty.
How Do You Remember the Difference Between "Fare" and "Fair"?
Now that we have gone over the definitions of fair and fare, let’s get into how you can remember the difference between each of these words. In this section, we’ll go over some tips on remembering the difference, show examples of both words in context, and even give you some practice sentences to test what you’ve learned.
Here are a few notes that might make it a bit easier for you:
Fair is more common, unless you are talking about food or transportation, so when you are in doubt, go with fair.
There is no such word as farely. So if you could make a sentence with the same meaning using an -ly word, then it is probably fair. For example, I could say, “I am fair today,” or I could say, “I am doing fairly well today.”
Fare is always a noun or a verb. So whenever you are using the word as an adjective or adverb, you know it must be fair.
What Are Some Examples of "Fair" and "Fare" in a Sentence?
Before I give you some sentences to practice with, let’s go back over some examples. In these, I’ll use the correctly spelled version of each word.
- I am going to the fair today. Have you been yet?
- Have you paid your bus fare yet?
- If you want to have your fair share of the prize, then you better put in a fair effort.
- I like bland food and simple fare.
- The fair lady fared well in her quest to find her knight in shining armor.
It is hard enough to keep homophones apart without adding in multiple definitions for each of the words. However, with a little bit of study, they don’t have to be so difficult. Hopefully, this post has helped you figure it out.
The good news is that if you still are a little confused, ProWritingAid is here to help. It’ll point out times where you may have used the wrong spelling of fair or fare. Additionally, you can use the Homonym Report to make sure everything is clear.
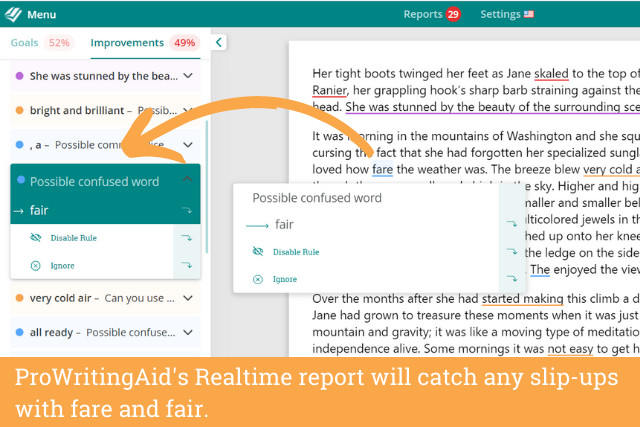
Check your spellings wherever you write with a free ProWritingAid account.
Quiz: Fair vs. Fare
Okay. Now it’s your turn! I am going to give you some fill-in-the-blank sentences. How many of them can you get right? (I’ll put the correct answers at the very end of this post.)
- Do you have enough money to cover the bus ...............?
- You always pick on me, and it isn’t ...............!
- This decision is as ............... as I can make it.
- I am cooking dinner tonight. What is your favorite kind of ...............?
- Is it ............... to ask how you ............... on the test?
How did you fare?
Answers: 1. Fare, 2. Fair, 3. Fair, 4. Fare, 5. Fair, Fared


