
“Passed” and “past” are homophones, which means that they have different definitions, even though they sound the same.
It’s easy to get the two mixed up when you’re writing. So how do you remember which spelling you should use?
The quick answer is that passed is the past tense of the verb “to pass," while past can mean many things.
Read on to see examples of each word in context, as well as tips for remembering which one to use.
What Does the Word Passed Mean?
“Passed” is the past tense form of the verb “to pass.”
When you add -ed to the end of the verb “pass,” you modify the meaning of the sentence to show that the event it's describing already happened. For example:
I pass the ball to my teammate (present tense) → I passed the ball to my teammate (past tense)
You pass the physics exam (present tense) → You passed the physics exam (past tense)
She passes me the gravy (present tense) → She passed me the gravy (past tense)

Here are some common phrases that include the word “passed,” all of which are the past tense:
- Passed away (present tense: pass away)
- Passed a test (present tense: pass a test)
- Passed the butter (present tense: pass the butter)
What Does the Word Past Mean?
The word “past” is a little trickier, because it has several different meanings. It can be used as a noun, an adjective, an adverb, or even a preposition.

As a noun, past refers to the period of time before the moment of speaking or writing.
You could say, It’s all in the past now, meaning that something happened so long ago that it's no longer relevant now.
As an adjective, past means "gone by in time and no longer existing."
You could say I’ve been really busy these past few days, meaning that you were really busy during the most recent couple of days that have gone by.

As a preposition, past means the same thing as "beyond" or "farther than."
You can say I think I drove past the destination already, meaning that you drove farther than you were supposed to.

Here are some common phrases that include the word “past”:
- The past (meaning: things that have already happened)
- Past tense (meaning: the grammatical tense referring to things that have already happened)
- Past caring (meaning: beyond caring)
- Past the sell by date (meaning: beyond the sell by date)
- Walked past / drove past (meaning: walked beyond or drove beyond)
- The past few days (meaning: the most recent couple of days)
- A quarter past noon (meaning: fifteen minutes after noon)
What Are Some Examples of Passed vs. Past in Writing?
Here are some examples of each word from literature.
Example Sentences with Passed
“What Is Love? I have met in the streets a very poor young man who was in love. His hat was old, his coat worn, the water passed through his shoes and the stars through his soul”—Victor Hugo, Les Miserables
“I am not talking to you now through the medium of custom, conventionalities, nor even of mortal flesh: it is my spirit that addresses your spirit; just as if both had passed through the grave, and we stood at God's feet, equal—as we are!”—Charlotte Bronte, Jane Eyre
“It's too late to change my mind. I lift my hand to my mouth taking one last look at the world. The berries have just passed my lips when the trumpets begin to blare.”—Suzanne Collins, The Hunger Games
Example Sentences with Past
“So we beat on, boats against the current, borne back ceaselessly into the past.”—F. Scott Fitzgerald, The Great Gatsby

“Who controls the past controls the future. Who controls the present controls the past.”—George Orwell, 1984
“Some birds are not meant to be caged, that's all. Their feathers are too bright, their songs too sweet and wild. So you let them go, or when you open the cage to feed them they somehow fly out past you.”—Stephen King, Rita Hayworth and Shawshank Redemption
What Tricks Can I Use to Figure Out Whether I Should Use Passed or Past?
Try Switching from Past Tense to Present Tense
If you’re wondering whether to use “passed” or “past,” you can try switching the word you're unsure about to “pass” or “passes” to see if it still makes sense in the sentence.
If it makes sense in present tense, you know you should be using “passed,” because it's the past tense form of "pass" or "passes."
Here are some examples:
I passed the ball to my teammate → I pass the ball to my teammate (correct)
You passed the physics exam → You pass the physics exam (correct)
She passed me the gravy → She passes me the gravy (correct)
On the other hand, if the word you're supposed to use is “past,” the sentence won't make much sense after you switch tenses.
For example, in this sentence describing a theatre trip ProWritingAid’s realtime report has identified an incorrect usage of the word pass and suggested that it be changed to past.
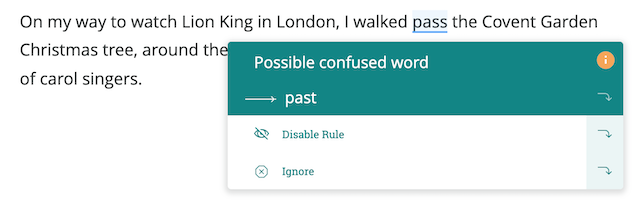
Here are some more examples:
I drove past the candy shop→ I drove pass the candy shop (incorrect)
This milk is past the sell by date → This milk is pass the sell by date (incorrect)
The present is more important than the past → The present is more important than the pass (incorrect)

Look for the Verb in the Sentence
A useful thing to remember is that the word “past” is never a verb. So if you’re using “past” as a verb, that’s a sign you might be spelling it wrong.
Try to find the verb in the sentence. You can do this by looking for an action.
If “passed” is the verb, then you're spelling it right. But if a different word is the verb, then you should use “past.”

Final Words: Passed vs. Past
What are your favorite tips for remembering the difference between “passed” and “past”? Let us know in the comments.


