One of the most powerful tools in a writer’s toolkit is point of view.
So, what is point of view in literature, and why is it important?
The short answer is that point of view, also called POV, refers to the angle from which a story is told. It includes the specific character who’s telling the story, as well as the way the author filters the story through that character to the reader.
This article will discuss the different points of view you can use in writing, including their strengths, weaknesses, and examples from literature.
What Is Point of View in Writing and Literature?
Point of view refers to the perspective through which a story is told.
To understand point of view, try this quick exercise. Imagine you’re telling a story about a well-traveled stranger who enters a small, rural town.
What are all the different perspectives you could tell this story from?
You might tell it from the perspective of the stranger who has never seen this town before and views all of its buildings and streets through fresh eyes.
You might tell it from the collective perspective of the townspeople, who are curious about who this stranger is and why he’s come to this part of the world.
You might even tell it from the perspective of an all-seeing entity, who can see into the minds of both the stranger and the townspeople, all at the same time.
Each of these options centers a different point of view—a different angle for the reader to approach the same story.
The Importance of Point of View
Point of view is one of the most important aspects of your story that you must decide before putting pen to paper (or fingers to keyboard). It can have an enormous impact on the tone, style, and even plot of the story.
Each point of view has its own strengths and limitations. In order to choose the right POV, you have to know what you want your story to accomplish.
For example, if you choose first person POV, you’ll be able to immerse the reader in a single character’s voice, humor, and worldview. On the other hand, you also have to show the world with that character’s biases and flawed observations.
The right POV can also completely change the way the story feels. POV is a matter of choice, but one that affects every part of your story or novel.
F. Scott Fitzgerald had to rewrite The Great Gatsby because he initially wrote it in Gatsby’s voice. He decided it would be much more powerful coming from Nick’s more naïve point of view. Imagine that masterpiece with a different point of view—it wouldn’t have the same objective, reliable feeling that it has now.
Summary of the Different Points of View
There are four main points of view that we’ll be discussing in this article: first person, second person, third person (with two subtypes: limited and omniscient), and fourth person.
- First person (“I pet the cat because I think it looks cute.”)
- Second person (“You pet the cat because you think it looks cute.”)
- Third person limited (“She pets the cat because she thinks it looks cute.”) and third person omniscient (“She pets the cat because she thinks it looks cute. Little does she know, this cat is actually an alien in disguise.”)
- Fourth person (“We pet the cat because we think it looks cute.”)

Read on to learn the strengths and weaknesses of each of these points of view.
First Person Point of View
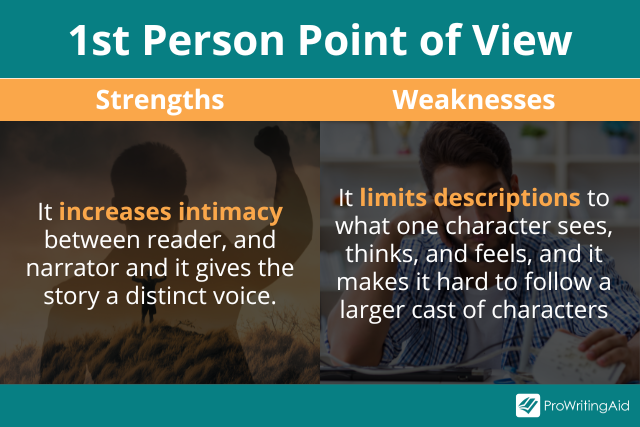
With first person point of view, everything is told intimately from the viewpoint of a character, usually your protagonist. The author uses the first person pronouns I and me to show readers what this character sees and thinks.
First person is the best way to show the story from one person’s point of view because you have an individual person telling you her story directly in her own words. It’s also the easiest way to tell a story that uses a distinct, quirky voice.
The limitations of first person point of view, however, restrict you to only describing what this character sees, thinks, and feels, and sometimes that narrator can be unreliable.
First Person POV Examples
One great example of first person POV is The Bell Jar by Sylvia Plath. The narrator is a flawed character, but we see the world entirely through her eyes, complete with her own faults and sorrows. Here’s a short excerpt:
“I began to think vodka was my drink at last. It didn’t taste like anything, but it went straight down into my stomach like a sword swallowers’ sword and made me feel powerful and godlike.”
Compare that with the intimacy you get when reading Scout’s view of things in Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird. She speaks with a childlike innocence, giving the reader that same feeling, even if we understand the racism of her town better than she does herself.
“We lived on the main residential street in town—Atticus, Jem and I, plus Calpurnia our cook. Jem and I found our father satisfactory: he played with us, read to us, and treated us with courteous detachment.”
Second Person Point of View
Second person point of view, which uses the pronoun you, is one of the least used POVs in literature because it places the reader in the hot seat and is hard to manage for a full-length novel. It’s used in experimental literature to try out new styles of writing.
In the wrong hands, it just feels gimmicky. But when done well, second person point of view can accomplish a range of wonderful effects.
Second Person POV Examples
“Story of Your Life” by Ted Chiang is a fantastic example of second person POV. It takes the form of a story a mother tells her daughter to explain the circumstances of the daughter’s life. Because the mother is speaking directly to the daughter, the story is imbued with an extra sense of intimacy.
“Right now your dad and I have been married for about two years, living on Ellis Avenue; when we move out you’ll still be too young to remember the house, but we’ll show you pictures of it, tell you stories about it.”
The Fifth Season by N.K. Jemisin is a Hugo-winning fantasy novel that uses many different POVs, including second person. The second person point of view serves to provide a feeling of disorientation, like the protagonist needs to talk to herself to remind herself what’s going on. Here’s a short excerpt from the very beginning of the story:
“You are she. She is you. You are Essun. Remember? The woman whose son is dead.”
Third Person Point of View
Third person point of view uses pronouns like he, she, and it. This POV allows the reader to follow a character, or multiple characters, from a more distanced perspective than first or second person.
Third Person Limited vs Third Person Omniscient
There are two subtypes of third person point of view: limited and omniscient.
In third person limited, the story follows only one character’s viewpoint throughout the entire piece. This means your reader sees only what the third person narrator sees and learns things at the same time the third person narrator does.
You can show what your main character thinks, feels, and sees, which helps close the emotional distance between your reader and the main character.
This is an excellent POV to use when your story focuses on a single character. In many ways, third person limited is quite similar to first person, even though it involves different pronouns.
The drawback with third person limited POV is that you can only follow one character. Showing other characters’ thoughts and feelings is a no-no.
The other type of third person POV is third person omniscient. In this POV, the story is told from the perspective of an omniscient narrator, who can see inside the heads of all the characters in the story.
This is a great POV to use when you have multiple characters, each with their own plot line to follow, and you want your reader to see everything as it unfolds. It’s also useful for imparting universal messages and philosophies, since the narrator can draw conclusions that no character would be able to on its own.
The downside to third person omniscient is that it can be emotionally distant from the story. Because you’re constantly jumping around to different characters and their story arcs, it’s harder for your reader to get as emotionally involved with your characters.

Third Person POV Examples
Examples of the third person limited POV are the Harry Potter novels. The reader sees everything that’s going on, but is limited to Harry’s point of view. We’re surprised when Harry is surprised, and we find out the resolution at the ending when Harry does. Here’s a short excerpt from the seventh book, Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows:
“Harry sat up and examined the jagged piece on which he had cut himself, seeing nothing but his own bright green eye reflected back at him.”
An excellent example of third person omniscient POV is Victor Hugo’s Les Miserables. The reader sees everything that is happening in the story and gets a vivid lesson in politics and society in France’s history.
“He was cunning, rapacious, indolent and shrewd, and by no means indifferent to maidservants, which was why his wife no longer kept any.”
Fourth Person Point of View
Fourth person is a newer POV that only recently started to be recognized as a distinct POV. It involves a collective perspective, using the plural pronouns we and us.
This POV allows you to tell a story from the perspective of a group, rather than an individual. Since there’s no singular narrative, this option is great for critiquing larger institutions and social norms. Fourth person is even rarer than second person, but when it’s done well, it can be very powerful.
Fourth Person POV Examples
“A Rose for Emily” by William Faulkner is told from the perspective of an entire town.
“We did not say she was crazy then. We believed she had to do that. We remembered all the young men her father had driven away, and we knew that with nothing left, she would have to cling to that which had robbed her, as people will.”
The Virgin Suicides by Jeffrey Eugenides is told from the perspective of a group of teenage boys.
“They were short, round-buttocked in denim, with roundish cheeks that recalled that same dorsal softness. Whenever we got a glimpse, their faces looked indecently revealed, as though we were used to seeing women in veils.”
What About Alternating Point of View?
You might choose to write a novel or story with multiple different points of view.
Some books have two main characters and switch back and forth between their perspectives—this is very common in the romance genre, for instance. Others rotate between three or more characters.

Alternating POV is a great option if your story features multiple main characters, all of whom play an equally important role in the story. The biggest drawback is that you risk confusing your reader when you switch back and forth.
Make sure your reader knows when you’re switching POVs. One common solution is to include a chapter break each time the perspective changes. Some books change the font for each POV, or even the color of the typeface.
It’s also important to make sure each character has a distinct voice. For example, maybe one character writes with short, brusque sentences, while another writes with long, flowery sentences. Keeping the different POVs distinct is crucial for success.
Conclusion on Point of View
There you have it—a complete guide to point of view and how to choose the right POV for your story.
Before you start experimenting with point of view, get comfortable with the basics first. Read works by authors who use these different POVs with great success to understand how each POV changes the narrative arc of the story.
Happy writing!

